The strenghts and weaknesses of proven radio protocols
WIRELESS M-BUS
Specifications
Wireless M-Bus is a standard European protocol. It is defined for the 868Mhz (25mw) and 169Mhz (25mw and 500mw) frequency bands. It is a point-to-point protocol between EndPoints and RF data hubs. The protocol is bi-directional subject to conditions, for each sent frame, the EndPoint listens for any frames sent by the hub for a few hundred ms.
The advantages:
- European standard (interoperability)
- Two frequency ranges (868Mhz and 169Mhz)
The weaknesses:
- Restricted range of available sensors
- Short range of about 800m
- Bi-directional subject to conditions
WAVENIS
Specifications
Wavenis is a proprietary protocol developed by Coronis (France) currently known as Elster.
It is defined for the 868Mhz frequency band at 25mw and 500mw. It is a fully bi-directional point-to-point protocol.
The advantages:
- A wide range of sensors
- Bi-directional, possibility of waking a sensor at all times
- Assets installed in France
The weaknesses:
- Not standardised
- Complicated consumption management
- Frozen protocol and products
ACTIVE RFID
Specifications
Short range 868Mhz sensors, low consumption and long service life. Point-to-point architecture with a central node (RF hub), property and people traceability application in an open building.
HOMERIDER
Specifications
Short range 868Mhz sensors, low consumption and long service life. The latest generation includes a physical LoRa layer and a proprietary protocol layer. Several million points operational, mainly in the water sector.



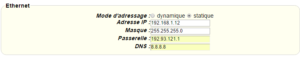
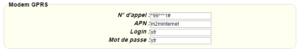
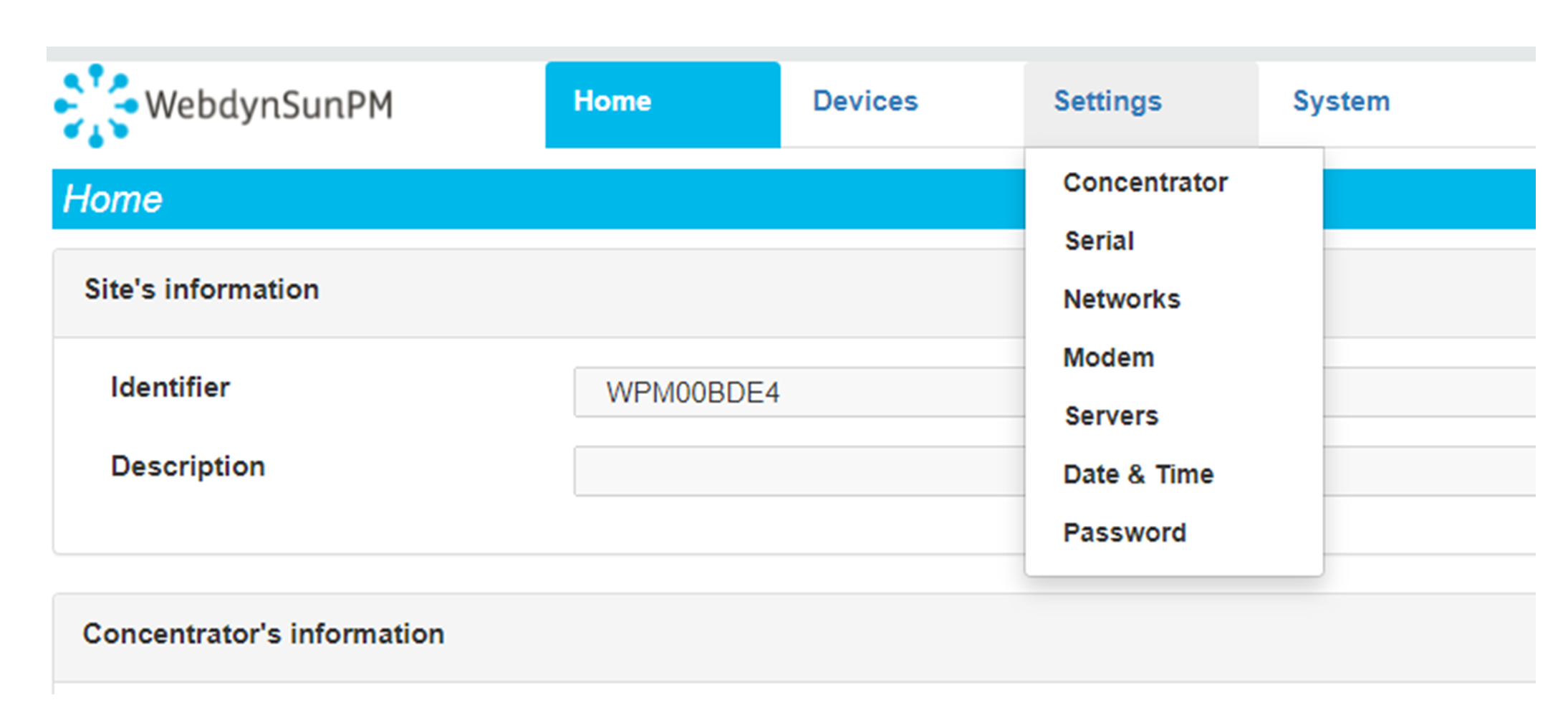 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
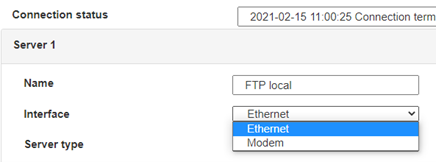 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
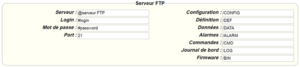
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
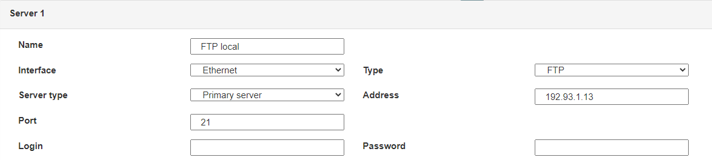 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.



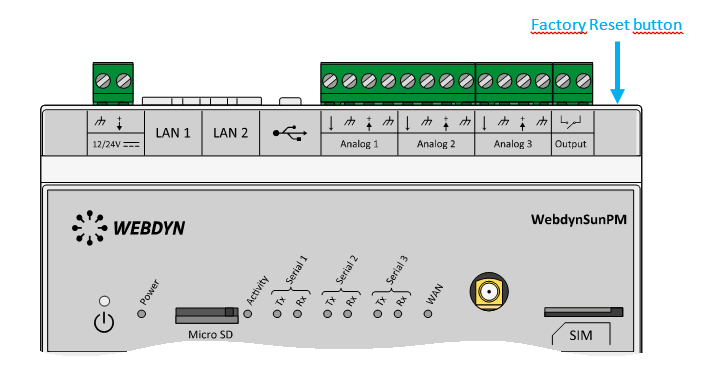 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.