Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
MTX-Tunnel needs special proprietary AT commands to allow MTX-Tunnel to be controlled by a third-party application, using a local serial port or 2G/3G/4G connection remotely. Please remember you can use one or two of the COM serial ports available. You can use them locally or you can use them remotely with IP (webserver, Telnet, MQTT, SNMP, gateway, etc.) and also SMS text messages. Please read carefully this AT special commands set features:
AT^MTXTUNNEL=END
This command stops and ends MTX-Tunnel Java program execution. MTX-Terminal modem is now in normal mode. This allows certain intelligent devices connected to MTX-Terminal to run or stop the MTX-Tunnel application and use the modem terminal for a voice call, CSD call, firmware upgrade… after this, MTX-Tunnel can be run again.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=VERSION
String returned is version information. Only for MTX-Tunnel V7 and above.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETBAUDRATE,port,speed
This command can change the modem serial port speed for a temporary amount of time, without the need for MTX-Tunnel to be reset. EXAMPLE AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETBAUDRATE, 0, 9600 ASC0 port baud rate speed is now 9600 bauds. AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETBAUDRATE, 1, 19200 ASC1 port speed is now 19200 bauds. Only for MTX-Tunnel V7 and above
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETPARAM,parameter_name
This command is intended to read or to find out a configuration parameter stored in a configuration file inside –non volatile memory-. For example, to read APN value stored in configuration file, use: AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETPARAM, GPRS_apn
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETCONFIG
This command is available for versions of MTX-Tunnel after v7.15. It returns the configuration file config. txt, avoiding the need for repeated use of AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETPARAM.
AT^MTXTUNNEL= SETPARAM,parameter_name,ValueParametro
This command is used to change any MTX-Tunnel configuration parameter value. For example, to change the baud rate of COM1 to 9600 bauds: AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETPARAM, COMM_baudrate, 9600 Please be sure to reset the MTX-Tunnel application to get the new configuration. The AT command to reset the terminal is AT+CFUN=1, 1
AT^MTXTUNNEL= SETPARAM,parameter_name1:parameter_value1rnparameter_name2:parameter_value2|rn.....parameter_nameN:parameter_valueN}
This command is used to change several parameter values at the same time. AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETPARAMS,{COMM_baudrate:9600rnCOMM_bitsperchar:8} Please be sure to reset the MTX-Tunnel application to get the new configuration. The AT command to reset the terminal is AT+CFUN=1, 1
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETIOS
This command gets readings from all GPIOs and ADCs of MTX-Terminals with MTX-Tunnel running. This is more convenient and faster than using one AT command for each GPIO/ADC, especially if you use SMS or GPRS connection for this. After execution, this AT command responds with each value in following order. Every state is separated by a “,” character: GPIO1,GPIO2,GPIO3,GPIO4,GPIO5,GPIO6,GPIO7,GPIO8,GPIO9,GPIO10,ADC1,ADC2
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETIO,numGPIO
This command returns the value of a digital input. NumGPIO indicates the GPIO number (1 to 10). Refer to GPIOs in the tables at the end of this manual for more information.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETADC,numADC
This command returns the value of a particular analog input. NumADC indicates the number of ADC (1,2). Refer to ADCs in the tables at the end of this manual for more information.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=RS232,mode,data
This command allows you to send and receive data directly from an MTX-Tunnel serial port. This is useful for end applications using WEB page forms; you can get the form values from the web page, collect them in the serial port, and after using them, send a response to the web page. You can see in Annex an example. Mode values: 0, 1, 2 or 3.
- 0: data is forwarded through COM1 without waiting for a response from the device connected to COM1, so there is no value response to this AT command.
- 1: data is forwarded through COM1 and will wait for a response from the device connected to COM1. This response will be the return value of this AT command.
- 2: data is forwarded through COM2 without waiting for a response from the device connected to COM2, so there is no value response to this AT command.
- 3: data is forwarded through COM2 and will wait for a response from the device connected to COM2. This response will be the return value of this AT command.
NOTE Mode value 1 and 3. Maximum device response is 160 characters long. data parameter is a text string sent though serial port.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SMS,phone_number,message
This proprietary AT command is intended to send SMS text messages. Do not use the AT+CMGS command as it is intended to be used in end-party applications. Parameters description: “phone number”: End user’s phone number “message” SMS text string
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETMODBUS,address;position1;data_1;data_2;...;data_n
When a MODBUS device is connected to secondary port on MTXTerminal, this proprietary AT command will allow some parameters stored in the memory table to change: address: modbus device address (0 … 255) position1: first position to write in modbus memory table data_1, data_2: data to be written in the Modbus on pointed position1 parameter Important: address, position1 and data_n are separated by “;”
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETMODBUS2,address;position1;command;data_1;data_2;...;data_n
When a MODBUS device is connected to secondary port on MTX-Tunnel, this proprietary AT command will allow some parameters stored in the memory table to change: address: modbus device address (0 … 255) position1: first position to write in modbus memory table command: it indicates the command to be used. It can be the command 15 (coils) or 16 (registries) data_1, data_2: data to be written in the Modbus on pointed position1 parameter Important: address, position1 and data_n are separated by “;”. This command can use the modbus command 15 or 16.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETMODBUS,address;position;numData;command
When a MODBUS device is connected to a secondary port on MTXTerminal, this proprietary AT command will allow you to read some parameters stored in the memory table: address: modbus device address (0 … 255) position: first position to write in modbus memory table numData: number of data to read from modbus table command: you can use the modbus command 3 or 4 Important: address, position and numData are separated by “;”
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETMODBUSALL
In this guide you will find many examples of scenarios where MTX-Tunnel is configured to read periodically the registries of one or many modbus slave devices. For example, you could configure MTXTunnel to read X devices every hour. But if at some point you want to launch a reading of all the Modbus devices configured (for example to make a test without waiting for 1 hour until the event happens) you can execute this AT command. It will immediately launch the process of modbus reading and sending the data to the server.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=TEMPORALCLIENT,IPaddress,TCPport,seconds
A new AT command that can create a temporal client TCP socket to a specific server IP address and port. Only use this when the MTX_mode parameter is “server” or “none”. Now you can send AT commands remotely, by simply using the special tags <MTXTUNNELR></MTXTUNNELR> Parameters: IPaddress: IP address (server) to be connected TCPport: TCP to be connected IMPORTANT. TEMPORAL client socket means it will be closed automatically if GPRS data is not sent or received within 60 seconds. The “seconds” parameter is available for versions of MTX-Tunnel after v7.15. It allows you to specify the number of seconds during which the socket will be open. If the command is resent with the seconds parameter as “0” once the socket is established, the temporal socket is immediately closed, without waiting for it to finish.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DELETEBBDD
Use this command when you need to delete the datalogger internal memory on MTX-Tunnel. After using it, the internal modem memory file “data.txt” will be deleted and the MTX-Terminal modem will be reset.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETIO,X,Y
MTX terminals that use 3G technology do not allow the use of the command AT^SSIO which is used in GPRS terminals to change a digital input. Instead, AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETIO,X,Y is to be used, where X is the GPIO to be changed (0,…,9) and Y the value to be assigned (0, 1)
AT^MTXTUNNEL=FTP, ftpServer, loginServerFTP, passwordServerFTP, directoriyFTP, remoteFilename, MTXFilename, NotificationURL
A FTP from a file saved on a remote server can be downloaded onto the MTX terminal, which can be used to change the configuration files “config.txt” and “operators.txt” or to download other times of files.
The server login and password must be inputted, along with the server directory where the file is located, its name in the server and the name to be used in the MTX device, and a URL that is notified when the download is carried out correctly.
EXAMPLE:
at^mtxtunnel=FTP,ftp.mydomain.com,myUser,myPass,folder1/folder2/,config.txt,config.txt,
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://www.myDomain.es/myPath,myUsername,myPassword,myOriginFile,myDestinationPath,myDestinationFile,timeOut
It is possible to make an HTTP/HTTPS download of a file set on a web server in the MTX terminal. It is useful to change the configuration file “config.txt”, change the file “iperators.txt” or download other kind of file.
EXAMPLES
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://myDomain.com/myPath,myUser,myPass,config. txt,,config.txt,30
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://myDomain.com/myPath,myUser,myPass,ServerCertificate1.jar,security/certs/servers/,ServerCertificate1.jar,30
Remember that if you change the configuration remotely, you must restart the MTX so it loads the new configuration (command AT+CFUN=1,1).
The time base for the timeOut parameter is seconds. This command will return OK or ERROR after downloading the file, not being able to send another command until the end of the same (download or timeout).
AT^MTXTUNNEL=ADOWNLOAD,http://www.myDomain.es/myPath,myUsername,myPassword,myOriginFile,myDestinationPath,myDestinationFile,timeOut
It is possible to perform an asynchronous HTTP / HTTPS download of a file located on a web server in the MTX terminal. Useful to change the configuration file “config.txt”, change the file “operators.txt” or download another type of file.
EXAMPLES
AT^MTXTUNNEL=ADOWNLOAD,http://myDomain.com/myPath,myUser,myPass,config.txt,,config.txt,30
AT^MTXTUNNEL=ADOWNLOAD,http://myDomain.com/myPath,myUser,myPass,ServerCertificate1.jar,security/certs/servers/,ServerCertificate1.jar,30
Remember that if you change the configuration remotely, you must restart the MTX for it to take the new configuration (command AT + CFUN = 1,1).
The time base for the timeOut parameter is seconds. This command will return OK or ERROR immediately while the file is downloaded in the background. Use the command AT ^ MTXTUNNEL = ISFILE to find out if the file has been downloaded.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=ISFILE,path,fileName
It allows to find out if there is a file inside the modem. Useful to use in conjunction with the AT ^ MTXTUNNEL = ADOWNLOAD command.
EXAMPLE
AT^MTXTUNNEL=isfile,,config.txt
This command will return OK if the file exists or ERROR if it does not exist.
If the file is in the root directory, leave the path field blank.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETCONFIGFILE,{ConfigRaw}
This command allows the entire content of MTX-Tunnel’s configuration file to be established without having to change each parameter one-by-one. It is designed to be used only from a Web platform as a response to the sending of a JSON object. For example, when MTX sends a JSON object from its internal logger to a Web platform, it can receive this command as a response between the <MTXTUNNELR> and </MTXTUNNELR> to change the complete configuration.
MTX will restart with the new configuration once the AT command is processed. The configuration must be between the {} tags.
The parameters can be sent separated by the sign “rn”.
EXAMPLE
{COMM_baudrate:9600rnCOMM_bitsperchar:8rn …………………}
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETOUTPUTTIMER,numOutput,value
This command allows a digital input or relay to be activated for X seconds using just one AT command. The output must be pre-configured with OUTPUT_mode in Timer mode (see example 8.5). numOutput is a value from 0 to 3, depending on the MTX model. Value can be either 0 or 1. The following AT commands are only used if the MTX_portAux value is configured to “wavenis”. You use it when MTX-IND-V1 and MTX-IND-V2 terminal modems are used with internal Wavenis card for concentrator scenario purposes and to allow communication via radio, with the modem and remote card sensor using Wavenis protocols.
AT^MTXTUNNEL= GETPOWERSTATUS
Command to state whether a MTX modem is being powered by an external power supply or by an internal battery. Only for modems with internal battery. Possible responses: -1 (ERROR), 0 (internal battery functioning), 1 (external power supply functioning).
AT^MTXTUNNEL= GETCELLID
Returns the identificator of the telephone cell being used. Useful for gsm localization systems.
AT^MTXTUNNEL= RESET,time
Resets the modem after the specific number of seconds indicated in “time” parameter (0, … 86400).
AT^MTXTUNNEL= getCounter,numCounter
Returns the current value of numCounter. The parameter “numCounter” can be 0 (in order to read counter number 1) or 1 (in order to read counter number 2). The returned value by the command is a value between 0 and 4294967294. Command exclusively valid for MTX-xG-Java-IoT.
AT^MTXTUNNEL= setCounter,numCounter,value
Sets the current value of a pulse counter. The parameter “numCounter” can be 0 (in order to update counter number 1) or 1 (in order to read counter number 2). The “value” field may have a value between 0 and 4294967294. Command exclusively valid for MTX models with pulse input counters like MTX-Java-IOT.
AT^MTXTUNNEL= setSchedule,ID:Day;Hour;Minute;ATCommand
Allows to configure an AT timing command for it to be executed on a certain day of the week (Monday, … Sunday) at a certain hour and minute. For example, it may be of use if you want to switch a relay or a digital output at certain hours. Remember that the modem uses UTC time. ID: 1 … 200. Timing index. 200 timings maximum. Day: 1…7. (1= Monday, 2=Tuesday, … , 7 = Saturday) Hour: 0…23 Minute: 0…59 ATCommand: execute AT Command EXAMPLE AT^MTXTUNNEL=setSchedule,1:2;22;0;AT^SSIO=0,1 (activates GPIO1 digital output every Tuesday at 22:00) This command will write to a file named “schedule.txt” that is inside the modem. There is also the possibility of upload the file into the modem by using a FTP server and the command AT^MTXTUNNEL=FTP, … The above mentioned “schedule.txt” file has the following format: 1:day;hour;minute;ATcommand 2:day;hour;minute;ATcommand 3:day;hour;minute;ATcommand If you want to delete a certain time setting, you can use “null” key in ATCommand field. For example, if you want to delete timing with ID=1: AT^MTXTUNNEL=setSchedule,1:2;22;0;null
AT^MTXTUNNEL=getSchedule,ID
Returns ID schedule of the modem, where ID = 1…200 indicates the schedule number.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=getSchedules
Returns a list with all scheduled time settings.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=delSchedules
Deletes all scheduled time settings.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=getAstronomic,latitude,longitude,dd,mm,yyyy
Returns the Ortho and Sunset for a given latitude, longitude, day, month, and year. Example for the city of Madrid: AT^MTXTUNNEL=getAstronomic,40.4893,-3.6827,12,03,2017
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETULPSECONDS,value
Command only for MTX models with ULP (Ultra Low Power). This command allows, once the modem is awake, to increase the time it stays awake or finish immediately. For example, you want to wake up the modem just 5 minutes every day to perform a task. The modem awakes and the task is completed in 2 minutes. Instead of waiting the remaining 3 minutes to enter ULP mode again, it can be shut down immediately specifying value 0, saving power. value: 0 … 86400 seconds
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,LISTSERVERS
It lists user SSL Root CA certificates for SSL connections. It lists the files available in the folder “secutity/certs/servers,” that is up to 10 possible files ServerCertificate1.jar, … ServerCertificate10.jar.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,INSTALLSERVERS
It installs all user SSL Root CA certificates for SSL connections. It installs the files available in the folder “secutity/certs/servers,” that is up to 10 possible files ServerCertificate1.jar, … ServerCertificate10.jar.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,DELETESERVER,certificateFile
It eliminates the SSL Root CA certificate indicated. The parameter “certificateFile” indicates one of the 10 possible certificate files ServerCertificate1.jar, … ServerCertificate10.jar that can be found in the directory “secutity/certs/servers” inside the modem. Once the command is executed the certificate is uninstalled and the file deleted from the directory.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,LISTCLIENTS
It lists client certificates for SSL connections (only needed if certificate client authentication is required from the server). It lists the files available in the folder “secutity/certs/servers,” that is up to 10 possible files ServerCertificate1.jar, … ServerCertificate10.jar.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE, INSTALLCLIENT,certificateFile
Unlike the certificates on the server, for which it is possible to install up to 10 at the same time, in the case of the client certificate, for obvious reasons it is only possible to install one certificate at a time. With this command it is specified the certificate to install.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,DELETECLIENT
It uninstalls the client certificate (but unlike the server certificate, it doesn’t delete any file from the directory “secutity/certs/servers”).
AT^MTXTUNNEL=CERTIFICATE,DELETEFILECLIENT,certificateFile
It deletes the indicated certificate from the directory “secutity/certs/servers.”
AT^MTXTUNNEL=setAstroSchedule,ID:Day;Month;SunriseHour;SunriseMinute; SunsetHour;SunsetMinute
Allows you to manually set the sunrise and sunset times for special days of the year (exceptions). In other words, if the astronomical clock is activated to act on a relay, it will switch based on the automatic calculations (sunrise / sunset) made by the modem, except for the times indicated by this command. This will allow you to set schedules for special days.
ID: 1 … 100. Temporization index, 100 schedules max.
Day: 1…31
Month: 1…12
SunriseHour: 0…23
SunriseMinute: 0…59
SunriseHour: 0…23
SunriseMinute: 0…59
Example:
AT^MTXTUNNEL= setAstroSchedule,1:15;7;8;30;21;45
(for July 15 the ortho will be at 8:30 and the sunset at 21:45)
This command will write to a file named “astroschedule.txt” found inside the modem. The entire copy of said file from an FTP server is also allowed using the command AT ^ MTXTUNNEL = FTP,…. Ó AT ^ MTXTUNNEL = DOWNLOAD…
The format of this file “astroschedule.txt” is as follows:
1:day;month;SunriseHour;SunriseMinute;SunsetHour;SunSetMinutern
2:day;month;SunriseHour;SunriseMinute;SunsetHour;SunSetMinutern
3:day;month;SunriseHour;SunriseMinute;SunsetHour;SunSetMinutern
…
AT^MTXTUNNEL=getAstroSchedule,ID
Returns the special astronomical programming modem ID, where ID = 1 … 100 indicates the exception number.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=getAstroSchedules
Returns a list with all the exceptions of the astronomical clock.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=delAstroSchedules
Removes all exceptions from the astronomical clock.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=delAstroSchedule,ID
Removes all exceptions from the modem’s astronomical clock ID, where ID = 1. 100 indicates the exception number.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,url,httpUsername,httpPassword,filename,modemPath,filenameDestination
Allows to download a file via http from a web server inside the modem.
Examples:
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://www.miweb.com,,,config.txt,,config.txt
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://www.miweb.com/miPath,,,astroschedule.txt,, astroschedule.txt
AT^MTXTUNNEL=DOWNLOAD,http://www.miweb.com/mipath,miuser,miPassord, config.txt, security/,config.txt
AT^MTXTUNNEL=IOEVENT
Starts a process of reading the modem’s I / O (digital inputs and outputs, analog inputs and pulse counters) to store them in the internal datalogger for later sending to a Web server or MQTT broker, without waiting for them to be produce an event or read period.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETIP
Returns the current IP address of the modem.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=EXECUTE,file
Run an AT command batch file. Inside the flash memory of the modem is a folder named “atscripts”. Batch files of AT commands can be incorporated into this folder to be executed using this command. In file the name of the file to be executed must be specified. See point 7.4 for more information.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=FORCEDNS
The DNS_ configuration parameters allow the modem to be configured to periodically send the modem status data (IP, coverage, GPIOs…). This command allows the immediate sending of the DNS frame without the need to end the configured period of time.
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETDAC,idDAC,valor
Command that allows changing the output value of a DAC for those modem models that have this interface.
idDAC: indica el identificador del DAC (0, …)
valor: valor en milivoltios a aplicar en el DAC (0 …10100 )
AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETDAC,idDAC
Command that allows reading the output value of a DAC of those modem models that have this interface. The returned value is in millivolts.
idDAC: indica el identificador del DAC (0, …)
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETIOMAINTENANCE,idGPIO,mode
Command that allows configuring an output type GPIO in maintenance mode. This allows you to temporarily leave the configuration mode to go into manual mode and be able to be activated / deactivated with the command AT ^ MTXTUNNEL = SETIO.
For example, consider a GPIO output configured as an astronomical clock. The output will activate with sunset and deactivate with sunrise. Activating the maintenance mode the output will go into manual mode until the maintenance mode is exited or the MTX modem is restarted.
idGPIO: indicates the identifier of the GPIO output (0, …)
mode: 0: normal working mode (the one configured in GPIO_config)
1: maintenance mode
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETWMBUSFILTERS,value
Command that allows activating or deactivating the configured manufacturer and device filters for reading W-MBUS sensors. Useful for commissioning of facilities where the MTX-Tunnel works as a W-MBus concentrator.
value:
0: Filters disabled
1: Filters enabled



 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
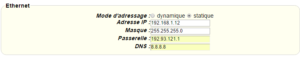
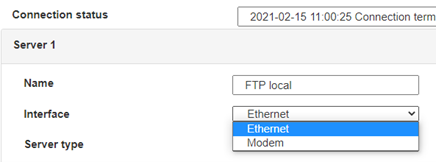 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
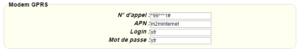
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
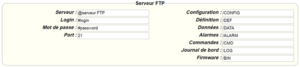
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
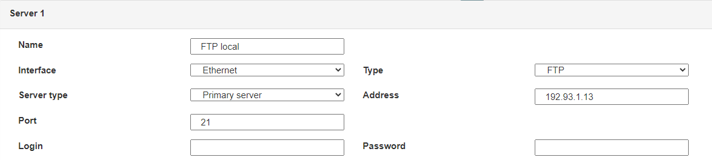 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
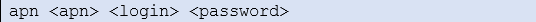



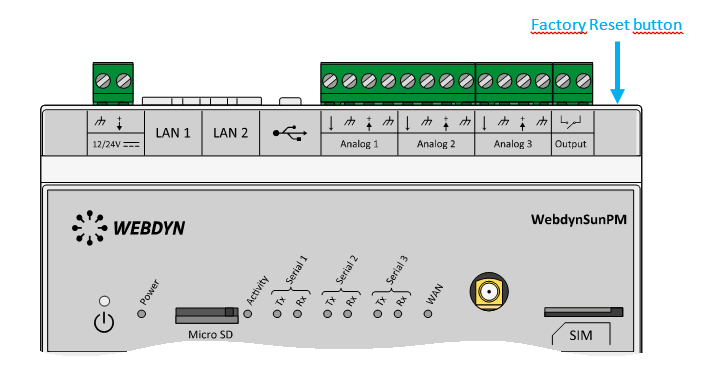 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.