Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
If still you have doubts about the new MTX-Tunnel please read the following FAQ section:
What is the MTX-Tunnel?
The MTX-Tunnel is an embedded software application that you can order from your distributor which is already installed into the MTX modems family.
What is the MTX-Tunnel for?
The MTX-Tunnel can be mainly used to create a transparent serial Gateway (or tunnel) 2G/3G/4G/GSM (RS232/485). If you already have a machine or device with a serial port and want to control them remotely as if it were physically connected to your computer, MTX-Tunnel is the solution you need.
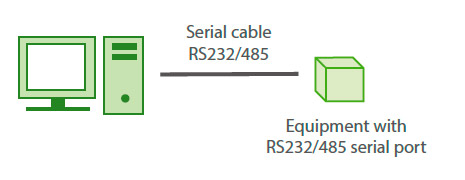
This is the scenario: serial equipment connected to a PC to read/write data…
With GPRS-Serial MTX-Tunnel gateway, the above scenario is shown in the following example. Now your PC has to establish a TCP/IP connection using MTX-Tunnel. Then, EVERYTHING you send to this TCP/IP connection will be sent to the equipment’s serial port by MTX-Tunnel. On the contrary, all of the information in the equipment’s serial port is sent to your server using the GPRS network.
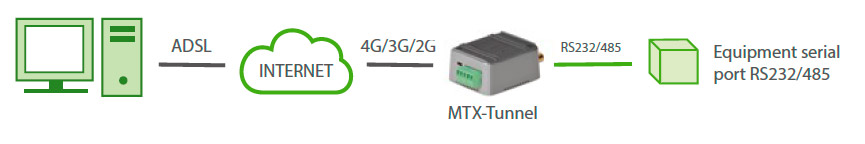
This feature (serial gateway 2G/3G/4G) is one of the many features that the MTX-Tunnel allows. Check the examples listed in this guide to grasp all the posibilities.
Is MTX-Tunnel needed at the PC server’s side?
It depends, but in general, it is not needed at the PC server’s side 99% of the time.
Not needed: If you already have your PC control software and have the option to connect via TCP/IP or UDP, a modem with MTX-Tunnel is not needed. Just configure the IP and the TCP port of the remote MTX-Tunnel and your PC will use the existing Internet connection to send and receive data remotely.
Not needed: If your PC control software does not have the option to connect using TCP/IP or UDP and the only option you have is to choose a COM port, the MTX-Tunnel modem is not needed. There are some freeware drivers for your operating system as Windows can emulate a COM port. Once this free driver is installed, a virtual COM (like COM100) will be installed in your PC and you must point to the IP and TCP port of the MTX-Tunnel remote. You must choose this virtual COM in your PC software.
Needed: If you need a “serial cable replacer” because you have to communicate two RS232 serial devices remotely and neither is a PC, i.e. you cannot install a virtual COM port because there is no operating system, you will need two MTX-Tunnels, one in each end. This is the scenario:

Who starts the connection?
MTX-Tunnel has the following modes TCP Server, TCP Client and UDP.
- TCP Server mode. MTX-Tunnel is waiting to receive incoming connections. This means that the remote device (PC server) will start and establish the 2G/3G/4G – Serial Gateway. (In newer versions of MTX-Tunnel, a temporary client socket can be created when there is no connection available and MTX-Tunnel receives data via the series port
- TCP Client mode. The MTX-Tunnel will start the Gateway. It will connect to the configured IP port of the server PC AND establish the GRPS-Serial Gateway automatically
- UDP mode. UDP is not oriented to connection protocol. MTX-Tunnel just waits for the UDP packet and sends them to the serial port and vice versa. The data present at the serial port is sent to a PC via UDP
It is mandatory to be permanently connected to GPRS?
No, it’s not.
If your application requires it (99% of the cases), MTX-Tunnel can always be connected to GPRS/3G. Remember that network operators will bill the data volume, not time.
If you do not need MTX-Tunnel to be connected 100% of the time and you want the connection to be sporadic, MTX-Tunnel can be activated in these ways:
- Missed call from authorized phone number
- Incoming SMS with the text “mtxtunnel on” from an authorized phone number
- By a change on the level of an input
- If the analog input is higher than the configured limits
- With any date/hour scheduled timing
- Just when data is present on RS232 port (only in TCP Server mode)
So… how long is MTX-Tunnel active for (4G/3G/GPRS connected)?
It is configurable by the GPRS_timeout parameter. You can specify the time in minutes after which, if no GPRS connection is detected, MTX-Tunnel will close the session.
I want to use MTX-Tunnel as a TCP Server so I can connect to it periodically from my PC. Will I need a SIM card with a fixed IP?
It is not mandatory. There are various ways of finding out the remote IP if using SIMs with normal dynamic IP addresses. You can either make a missed call or send an SMS with the word “mtxtunnel on” to the remote MTX-Tunnel equipments. MTX-Tunnel will reply with an SMS including the IP obtained at this moment in time.
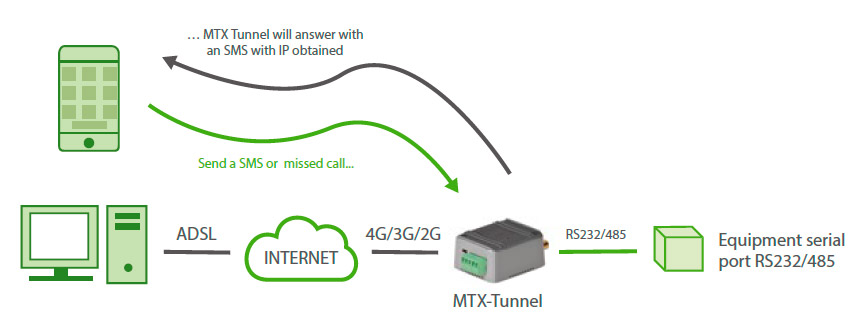
The new MTX-Tunnel is DynDNS featured. DynDNS is a service allowing you to associate a DNS name (like modem1.dyndns.org) to the IP obtained by MTX-Tunnel. For now, you can use this service for free: www.dyndns.org. It is also fully compatible with the free service offered by No-IP (www.no-ip.com).
Keep in mind that these services are NOT offered by MTX-Tunnel; we do not offer support and we are not responsible for these third party services.
I found that in my case I’m going to use thousands of MTX-Tunnel devices. I cannot use missed calls or SMSs to work out IP addresses. I do not want to use DynDNS as it can be difficult to handle and even costly. What can I do?
The MTX-Tunnel can inform the server PC every time an IP address changes.
You just need to enable a configuration parameter so that each time MTX-Tunnel changes the IP it will send frame data to a server PC with the following information: IMEI, the newly obtained IP and an optional user-configurable text.
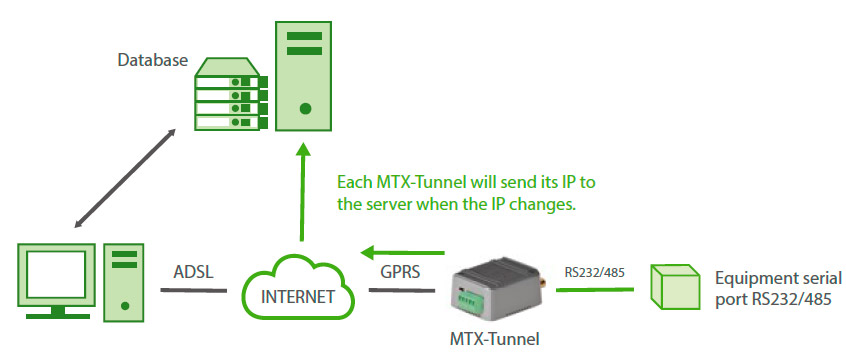
Is it possible to send the new IP to a Web server? I’m more familiar with Web programming – ASP, PHP – rather than TCP-IP sockets. I’m thinking about using a database. Is this possible?
Yes, it does support this protocol conversion.
And via MQTT/MQTTS?
Yes, it can configure a TOPIC in the MTX-Tunnel to inform about the IP change (it can include other data like the digital inputs status, counters, analog inputs, etc.).
You are talking about relays, analog inputs… Is MTX-Tunnel not a Serial-GPRS Gateway?
MTX-Tunnel is a serial-GPRS Gateway but can also simultaneouslycontrol digital inputs/outputs, analog inputs, relays, GPS receivers, and devices connected to SPI/I2C, as well as read modbus series devices and 868MHz radio devices.
For example,the MTX-Tunnel can remotely read a digital input or commute remotely with a relay. It can also send automatically, at a pre-configured time of every X seconds.
Also, it can send automatically, at a pre-configured time of every X seconds, the status of all inputs/outputs or the GPS position to a server PC or WebServer. SMS messages can also be used. It can also remotely read a sensor connected to SPI or I2C. See the example annex for more information.
I’ve read about sending AT commands using a TCP/IP connection. Can I use an AT command to change the value of a digital output?
Yes, you can send AT commands via TCP/IP; you can also send them from a normal modem, via serial ports or you can send them via SMS. You can also activate relays or read or write digital input/outputs on your Web page (see API section 7 and example scenarios)
So, using MTX-IND, I can activate a relay using a SMS, but… it is impractical because the AT commands are not intuitive nor easy to remember.
Yes. It is possible to send AT commands via SMS and therefore activate a relay; however, it is not necessary to send the exact AT command. MTX-Tunnel supports ALIAS which means you can configure the modem to understand the SMS with the text “RELE1ON” as the command “AT^SSIO=0,0”, which activates Relay #1. Up to 10 ALIAS strings can be created.
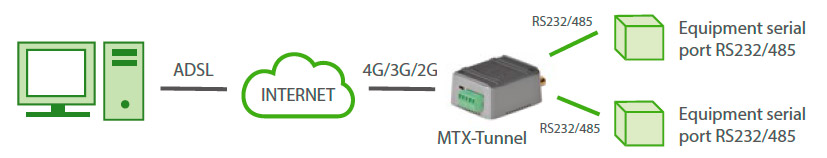
Could I control two RS232 external devices with one terminal?
Yes, you can. MTX-Tunnel can control two RS232 external devices with just one SIM card. MTX-Tunnel will create two serial-GPRS tunnels running in parallel.
Just remember that the MTX-65i, and MTX-65i-ULP modems only have the TX and RX lines and therefore the secondary port cannot use flow control because the do not have the CTS and RTS lines; they only have the TX and RX lines.
See a configuration example: An advanced example for reading 2 serial devices using a single modem/SIM and simultaneously using GPRS connection and GSM calls. There is additional serial tunnelling when there are no GSM/ GPRS connections
What about using the MTX-Tunnel in a modem with GPS receiver inside? Can I use it for fleet management?
It is not intended for professional fleet management. The possibility of installing the MTXTunnel on modem witg GPS receiver inside exists so that the GPS position can be read in any given moment, i.e. the location of the modem can always be known, be it through requesting it via IP, WebServer, Telnet or SMS.
MTX-Tunnel can be configured to automatically send the GPS position every X seconds. However, MTX-Tunnel does not internally store the position in the Flash memory. This means that if there is no GPRS network and the GPS position cannot be sent in the given moment, the positions will not be stored for sending when the network coverage is restored. This is a typical application if GPRS coverage is lost. Because of this, it can only be used for basic fleet management as professional systems usually store the GPS position points like a data logger for future sending.
What is WebServer used for?
MTX-Tunnel WebServer which is included can be used to read the digital input/outputs or analog inputs and to change digital outputs easily on a PC (connected to the Internet) using a standard Internet browser.
Not only this, you can remotely see and modify the MTX-Tunnel’s configuration parameters. Also you can execute AT remote commands, like network coverage (using the command AT+CSQ), check incoming SMS, etc.
What is Telnet used for?
You can basically do the same with the Telnet service in MTX-Tunnel as you can with WebServer but it is more commonly used for third party application integration. Please read the TELNET and API section.
If you are unsure about whether to use WebServer or Telnet, we recommend Telnet since the remote access is much quicker.
I’m worried about unauthorized access using WebServer or Telnet.
MTX-Tunnel has an internal firewall which can be activated. Then MTX-Tunnel will only accept connections from previously configured IP addresses. Any other IP addresses will be blocked. Check the parameters FIREWALL_ in this guide.
For maintenance purposes, I would like access to MTX-Tunnel at any time and in any location, from any IP address.
In this case Firewall WebServer can be disabled, but we recommend protecting the WebServer with a user Login and Password. MTX-Tunnel can work with or without a Login/Password (public WebServer). The same applies for Telnet.
Could I or somebody else receive an SMS when an input changes, like alarm detection?
You can configure MTX-Tunnel to send special and configured SMS text strings to up to 10 configured different phone numbers. The SMS text can be configured in different text strings related to digital or analog input.
MTX-Tunnel is a GRPS-Serial tunnel Gateway. What is a GRPS-I2C, GPRS-SPI, HTTP-Serial or SMS-Serial tunnel? Do you have some examples?
EXAMPLES:
GPRS-I2C Tunnel: You can read an I2C sensor remotely like a temperature sensor.
GPRS-SPI Tunnel: You can write data on SPI bus and if a display is connected to it, the data will be on display.
HTTP-Serial Tunnel: You have a Web page with a form. All filled form data can be sent to the serial port of the device connected to the MTX-Tunnel. Then MTX-Tunnel will collect the machine response and send the data as a web response to your Web page.
SMS-Serial Tunnel: Example. You can define special text like “MTX” at the beginning of the SMS string. The text after this special string will be redirected to the serial port of the machine. MTX-Tunnel can extract the response from the machine and send another SMS to the user. For example: for the SMS “MTX 12345”, MTX-Tunnel will send the string “12345” to the serial port and will get a response from the machine like “67890”, which will be sent as SMS.
I need a low power application terminal modem. What can MTX-Tunnel do?
It allows the modem to be switched off completely until an event happens. This way the power consumption is about 2 uA. The modem is off and cannot do anything. It cannot receive calls, SMSs or communicate at all. Therefore an event needs to happen.
This event can be a digital input level change or a periodic alarm. As an example, MTX-Tunnel can be configured to wake up every 24 hours, send the telemetry (all the inputs values, RS232…) and after five minutes of being awake in case it needed to communicate with a serial equipment connected to the MTX-Tunnel, the terminal will be automatically switched off for another 24 hours.
Is it also possible to define scheduled wake up tasks. For example, the modem can wake up for X minutes every day at 10.00 AM or only on the 1st and 15th days of the current month at 08.00am and 08.00pm, or as needed.
If MTX-Tunnel can be woken up in a configured time, does this mean that there is clock inside? But you can also say that it’s powered off. Please explain.
ULP modems have their own Real Time Clock that allows to them to wake up at a configured/scheduled time/date.
Does the clock lose time? How can I assure that it always keeps time? that there is clock inside? But you can also say that it’s powered off. Please explain.
MTX-Tunnel includes time synchronization via 2G/3G/4G; in fact, it is mandatory to use it if the RTC is to be used. This way, each time a connection to the 2G/3G/4G is made, another is also made to a time server to synchronize the time and ensure it is always accurate (to UTC time). It is also mandatory to use the time server when using the Datalogger function that is included in MTX-Tunnel.
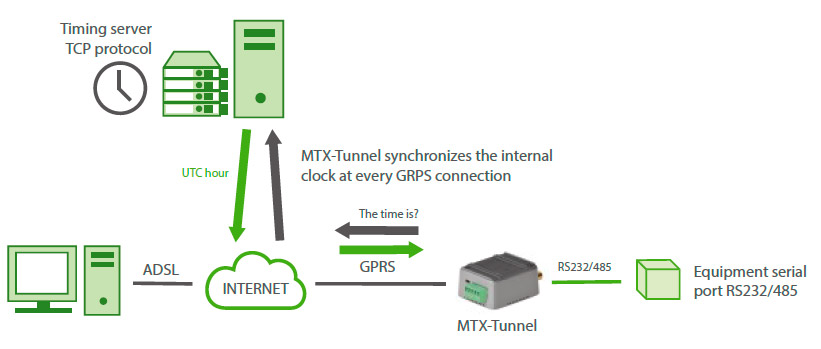
MTX-Tunnel used on the MTX-65-ULP wakes up at configured day/hour for some time (x minutes). Will the GPRS-Serial Gateway be active at this time?
During wake-up time, the modem will start and will run all configured services (WebServer, Telnet, Input/output telemetries…). In case the 2G/3G/4G serial tunnel is configured, it will activate it, but in case the WebServer is, it will activate, same with Telnet, if it has to send the digital I/Os, or if it needs to read an RTU Modbus device, it will also do it during that time.
What about SSL security? How does it work?
Some applications need some encryption data transmission. SSL is used. This way the data is transmitted and received SSL encrypted, avoiding data recovering sniffer. SSK is only available in TCP client mode. Be sure that your server can support SSL sockets in the following specifications:
- TLS Protocol Version 1.0 as RFC 2246.
- SSL V3 as The SSL Protocol Version 3.0
- WAP(TM) TLS Profile and Tunneling Specification as WAP-219-TLS-20010411-a
It is also possible to send data via HTTPS for sending telemetries over secure web servers. Same to send data via MQTTS.
From the MTX-Tunnel v10 on it is also possible to include in the modem up to 10 SSL Root CA certificates, as well as an SSL client certificate if needed.
What does “API” feature mean?
API is mainly a way to integrate MTX-Tunnel in end user application. Basically it is like a special AT command end user. It can be easily integrated in a web page and can also switch a relay (change an Output) for example.
API could also be used to remotely access the MTX configuration and send AT commands at the same time without knowing all of the configuration parameter syntax.
What does “API” feature mean?
API is mainly a way to integrate MTX-Tunnel in end user application. Basically it is like a special AT command end user. It can be easily integrated in a web page and can also switch a relay (change an Output) for example.
API could also be used to remotely access the MTX configuration and send AT commands at the same time without knowing all of the configuration parameter syntax.
Please explain what MTX-Tunnel is able to do with a ModBus device connected to serial port on MTX-Terminal.
MTX-Tunnel will periodically and independently request data to the ModBus device connected to serial port. It will store the data in the internal memory and it will send the data to an http web server encapsulated in a JSON object. In any case the internal buffer is 1500 long which allows it to store data in case of network or coverage loss. The readings will be re-sent when the modem connectivity problems are resolved.
Is it possible to access the advice via GPRS and GSM at the same time?
Indeed, since MTX-Tunnelv7.11 it has been possible to establish gateways with both at the same time, but GSM calls have priority. A typical is example is that of an energy operator (Endesa, Iberdrola…). They could want daily access to a meter to take a reading via GSM but you also want to be able to access the meter but via GPRS, MTX-Tunnel allows you to do this. Remember MTX-2G-IoT does not support GSM calls made from analog modems. If you configure a 3G device to receive analog calls it must be set to work in 2G mode with the parameter GPRS_mode: 2g
How to configure a specific scenario
The new MTX-Tunnel has a lot of configuration parameters, more than explained in the FAQ section. Take a look in the configuration section.
Next you can find step-by-step MTX-Tunnel examples of first configuration scenarios; they are very useful for you for first hands-on usage.
In the Annex there are lots of examples of scenarios with the appropriate configuration to get MTX-Tunnel working. Try to find the closest scenario to you and review the copy & paste selected configuration, it’s nothing more special than that.
If you have specific questions contact the support line iotsupport@matrix.es.



 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
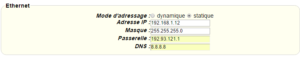
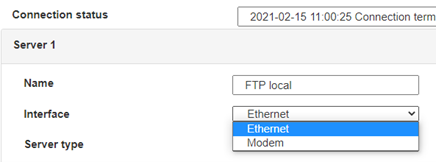 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
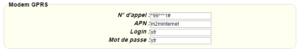
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
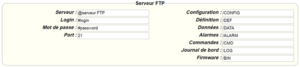
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
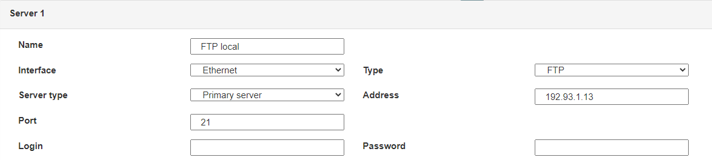 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
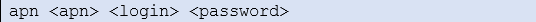



 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.