Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
Scene Details
Titan routers have the funcionalities a 2G/3G/4G router has, plus a variety of features that make it one of the most functional routers in the marketplace. One of those features is the ability to function as a concentrator of data coming from sensors (modbus, Wavenis radio, Wireless-Mbus, temperature…).
To send this data to a server we can send the data via HTTP/HTTPS, MQTT/MQTTS or even FTP. There are many application notes about this topic, like AN4, AN6, AN14, AN15, AN21, AN24, AN26, AN27, AN32, AN34 etc. After reading them we can configure the Titan router to gather and send data.
The Titan router can be configured to send data through Ethernet or WiFi interfaces, which will be explained on this application note.
Table of Contents
Sending Data via Ethernet Interface Using ADSL/Fiber Router
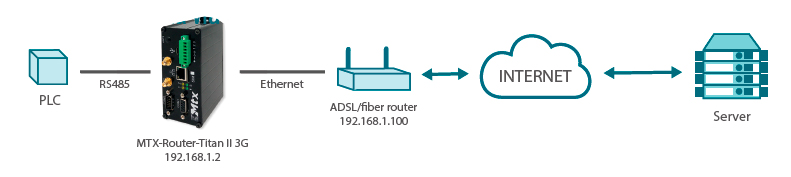
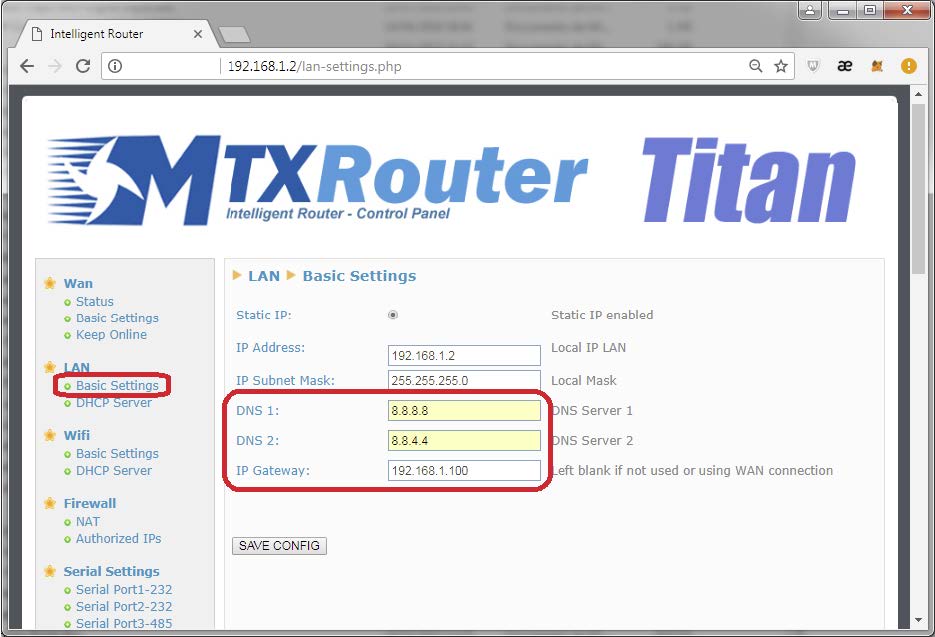
The configuration of the Titan router for this scenario is very simple. When the 3G interface is disabled, we need to configure the section LAN > Basic Settings, by appropriately setting the gateway IP address (where we will specify the LAN IP address of the router connected to the Internet, in this example 192.168.1.100) and the DNS (in this case we will use those from Google: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
Configuration to Send Data via WiFi Using ADSL/Fiber Router

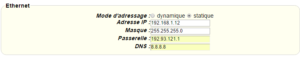
The configuration of the Titan router for this scenario is also simple. When the 3G interface is disabled, we need to go to the section WiFi > Basic Settings. In here we will need to enter all the data needed, like “WiFi Client,” specifying the SSID of the ADSL/fiber router (with WiFi) who gives Internet access, and the kind of security password. Once this is done, we have two options. On one hand we can configure the “IP Model” field in the Titan router as “dynamic.” This way the Titan router gets its IP, gateway IP and DNS from the DHCP server of the existent ADSL/fiber router. This can be done as seen on the screenshot below:
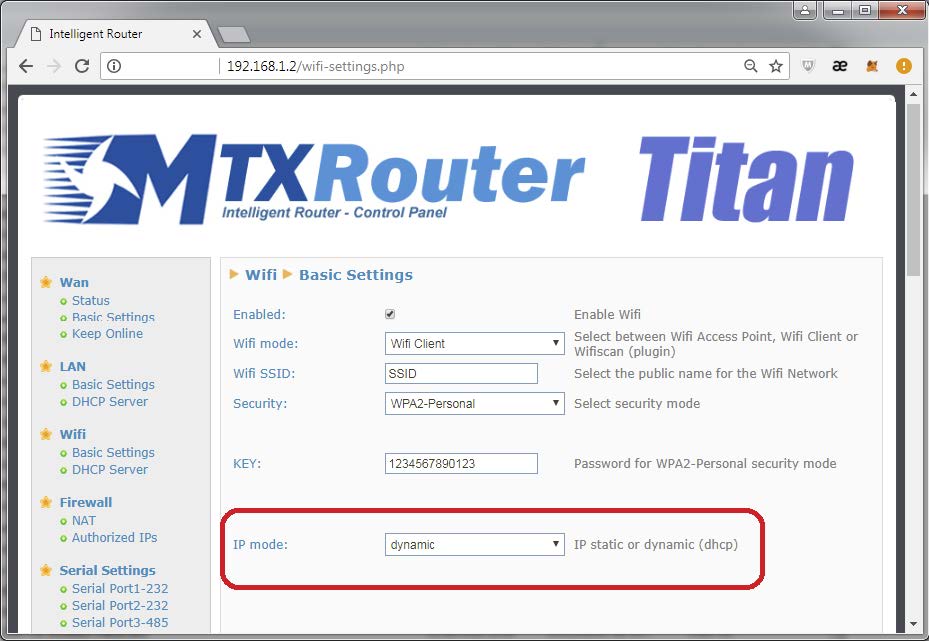
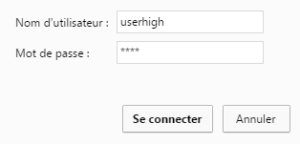
Then we need to change the password. To do that we go to “Other > Password” and click on “Save Admin Pass” to save the changes.
On the other hand we can configure the Titan router to assign a static WiFi IP address. To do this we need to select the option “static” on the field “IP Mode” and, as in the Ethernet case, we enter the DNS and IP gateway data.
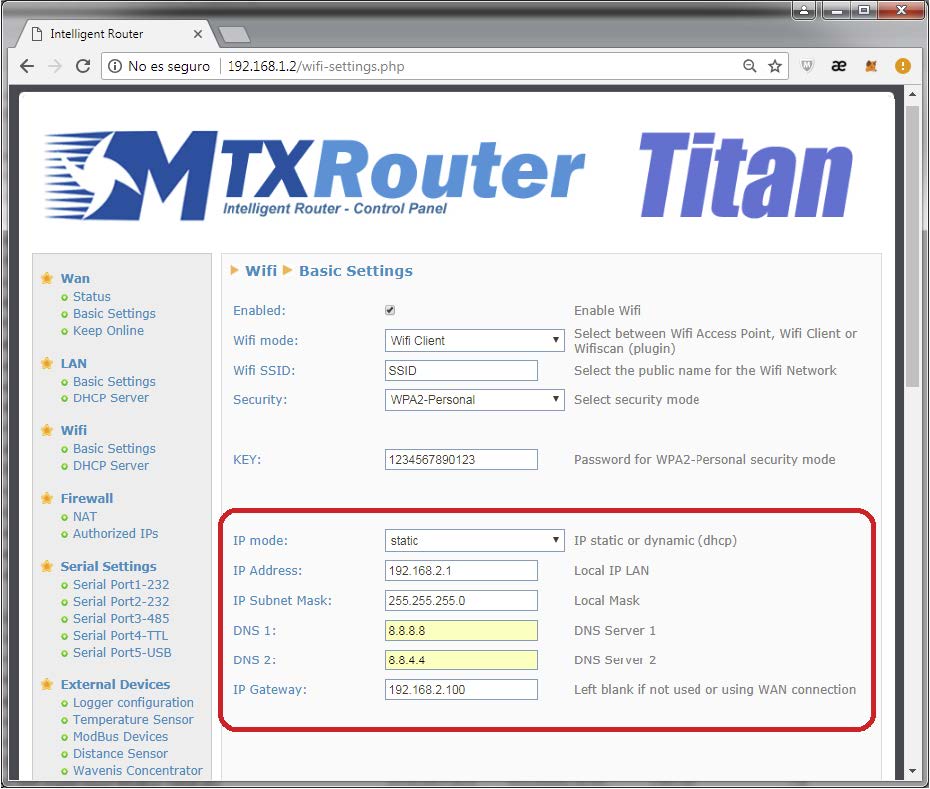
We need to have in mind that the WiFi interface must have a different subnetwork from that of the interface. For example, if the Ethernet interface belongs to the subnetwork 192.168.1.X/24, the WiFi interface can’t belong to the same subnetwork. A correct configuration, as the one done in this example, would be to configure the WiFi interface as 192.168.2.X/24.
In case we use WiFi in dynamic mode (DHCP), we need to make sure the IP assigned by the DHCP to the Titan router doesn’t belong to the subnetwork used by the Ethernet interface. If that’s the case, the Ethernet OP of the Titan router must be modified to another subnetwork.



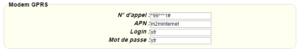
 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
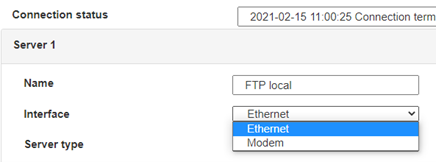 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
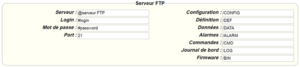
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
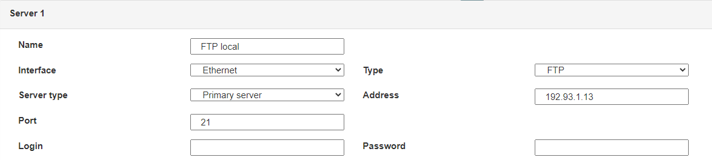 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
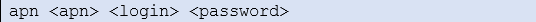



 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.