Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
Table of Contents
Scenario Details
This Application Note is a step-by-step guide that allows you to check the OpenVPN functionality of the Titan router series. Digital Certificate examples will be used throughout. These can be downloaded from the Titan router. However, it is recommended that the user generate his/her own certificates in order to have a real application.
The following example will be used as the base for this step-by-step guide:

In other words, this example aims to access the PLC from the PC Server with OpenVPN as if it were connected to the local network, and vice versa (accessing the PC Server with OpenVPN from the PLC). By using OpenVPN, we will be able to link the two, independent of the type of IP provided by the GSM operator (fixed IP, dynamic IP, public IP, private IP, etc.).
Configuration and Pre-requisites
Despite a SIM card providing a fixed IP address not being necessary, it is highly recommendable that the IP address of the company’s ADSL router (where the PC Server with OpenVPN is installed) has a fixed IP address, which is already common practice in many companies.
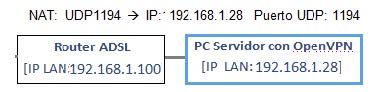
To configure an OpenVPN, we will use a standard UDP port 1194. Therefore, the only requisite is that the ADSL Router is routed using a NAT from the 1194 port to the same port of the LAN IP on the PC Server with OpenVPN.
192.168.1.28
Installing OpenVPN on the PC Server
First of all, we need to install OpenVPN on the PC server. For a Windows OS, which we will use in this example, the following software can be installed:
http://swupdate.openvpn.org/community/releases/openvpn-2.2.2-install.exe
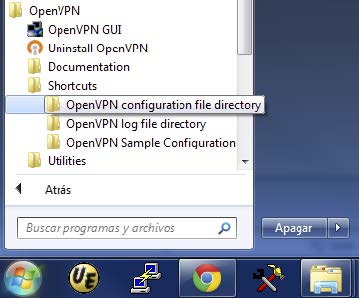
Once installed, we need to click ‘Start’ and open the folder that directs us to the link “OpenVPN configuration file directory”
In this directory there are several items:
- Copy the files (certificates and keys) ca.crt, server.crt, server.key and dh1024.pem For evaluative purposes only, these files can be downloaded from the following links:
ca.crt: https://www.dropbox.com/s/nxzmm4f4722plh4/ca.crt?dl=0
server.crt: https://www.dropbox.com/s/fuv652runkouwjk/server.crt?dl=0
server.key https://www.dropbox.com/s/yseozxs5icpt58z/server.key?dl=0
dh1024.pem https://www.dropbox.com/s/vcwby4y636thzoy/dh1024.pem?dl=0 - Copy to the directory the configuration file for the OpenVPN server. The following example can be used for evaluative purposes:
config.ovpn https://www.dropbox.com/s/y23owbh0gacipmj/config.ovpn?dl=0 - Create a folder called “CCD” inside the last folder. Here we will place the file “client1” (thedefault name used when the client certificate was generated). This file can be downloaded from the following link:
client1 https://www.dropbox.com/s/0c8d43mkps2gf12/client1?dl=0
Once completed, the server is configured and the only thing remaining is to execute it. To do this, we need to go to the Start menu and execute “OpenVPN GUI”.
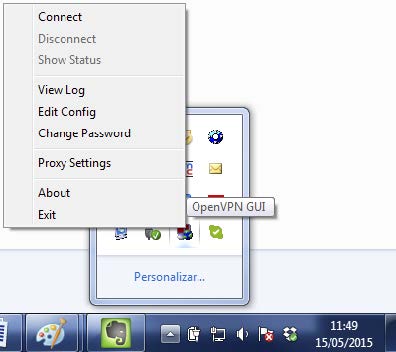
Upon launching, an icon will appear in the task bar next to the clock. Select ‘Connect’. The Open Server is now running, awaiting remote connections from OpenVPN.
Configuring OpenVPN on an MTX-Router-Titan-3G Device
Configuring the client is simple. The router is pre-configured with a LAN IP 192.168.2.2 and 3G connectivity. To configure the VPN, we need to enter the following configuration at “VPN > OpenVPN Client”:
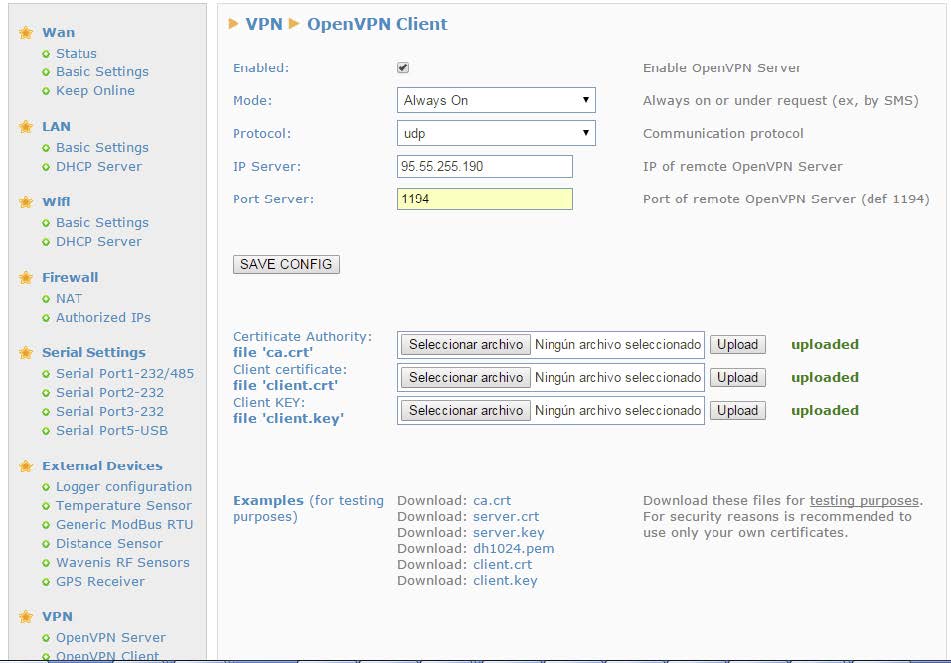
The certificates and keys “ca.crt”, “client.crt” and “client.key” must be uploaded. For this example only, these files can be downloaded directly from the configuration page of the router, or via the following links:
ca.crt: https://www.dropbox.com/s/nxzmm4f4722plh4/ca.crt?dl=0
client.crt: https://www.dropbox.com/s/d0io4wdnq527zo0/client.crt?dl=0
client.key https://www.dropbox.com/s/yg6k55qkytamd2v/client.key?dl=0
Following this, we must edit the Server IP with the public IP address of the ADSL router which the MTX router will connect to. Then we must restart the router, after which the VPN will establish a connection as can be seen in the OpenVPN server log.
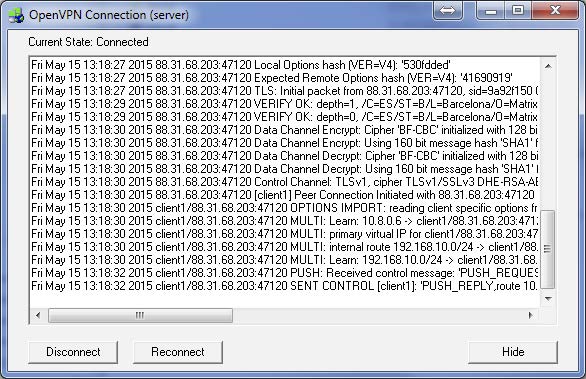
Following this, we must edit the Server IP with the public IP address of the ADSL router which the MTX router will connect to. Then we must restart the router, after which the VPN will establish a connection as can be seen in the OpenVPN server log.
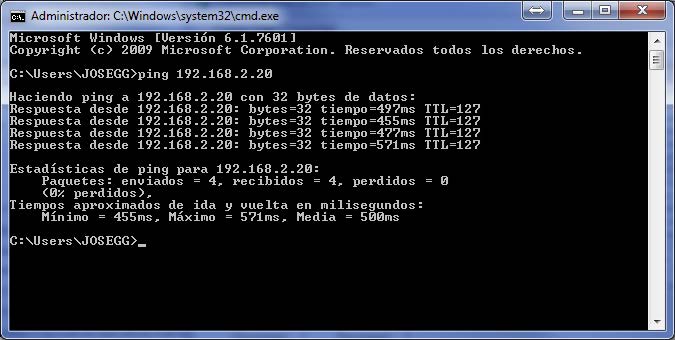
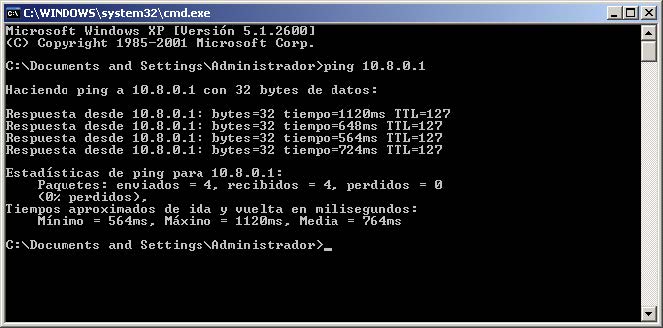
Finally, if you wish to connect in the opposite direction (from the remote device to OpenVPN’s PC Server), this must be done to the IP configured in the file we previously used (config.ovpn), which, in this case, has an IP 10.8.0.1. Therefore, if we send a ping in the direction 10.8.0.1 (the address assigned to the OpenVPN server), we will also receive a response as below:
Problems
If it does not work, check the following:
- The IP Gateway assigned to the remote PLC (192.168.2.20) must correspond to the local IP of the router (192.168.2.2).
- There should not be a firewall or antivirus installed on OpenVPN’s PC Server that could block the connection to the VPN ports (UDP1194 in the case of this example).
- Check that the NAT in the ADSL router is correctly configured.
Remember
It is necessary for the user to create their own certifications for real applications. Instructions of how to do this can be found at the following link: https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/howto.html



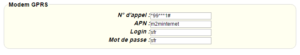
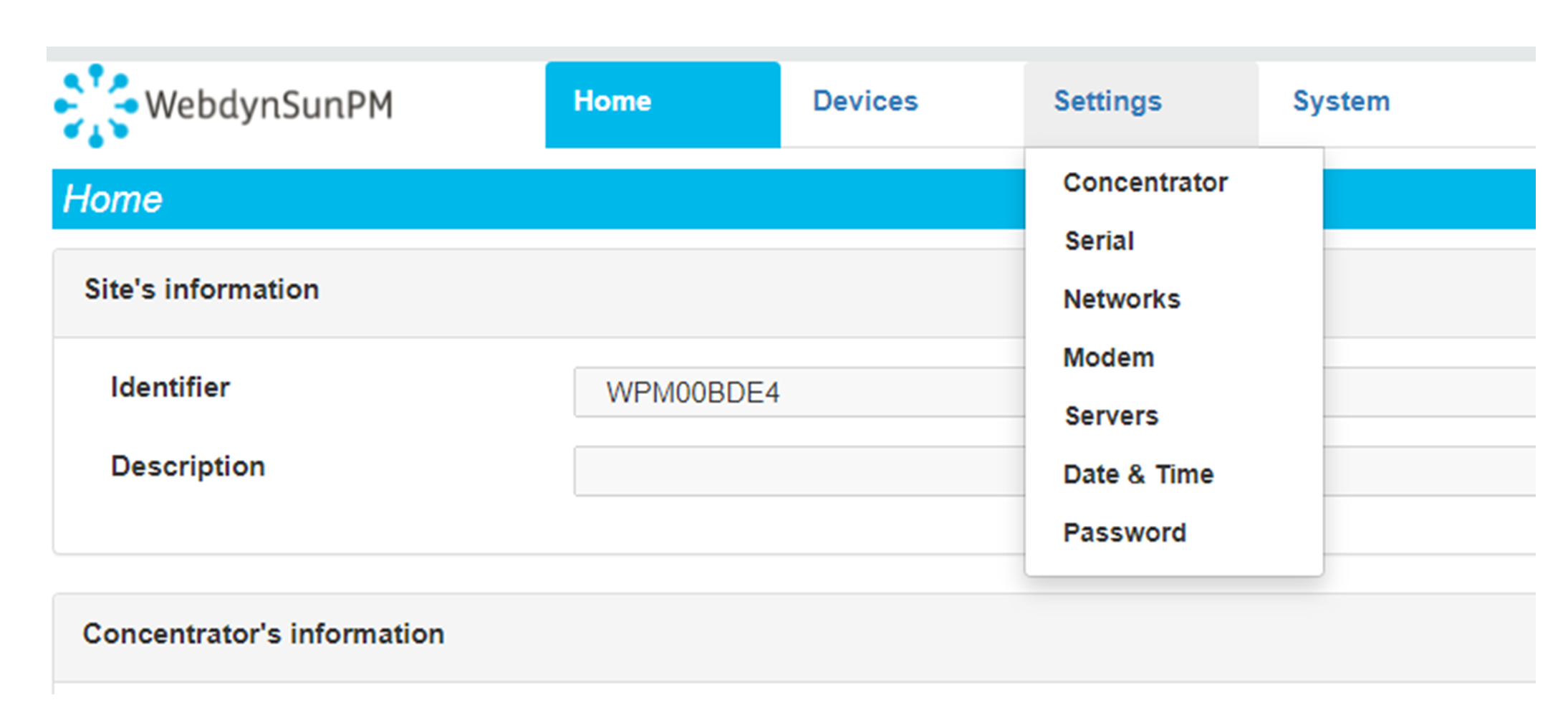 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
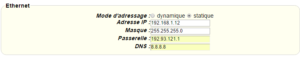
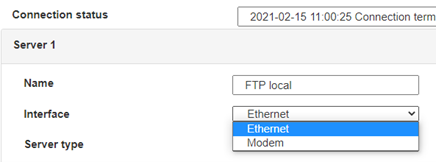 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
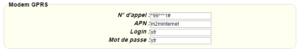
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
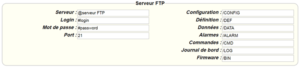
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
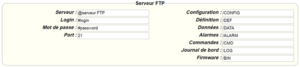
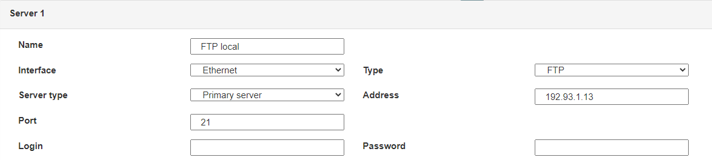 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
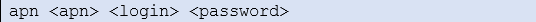



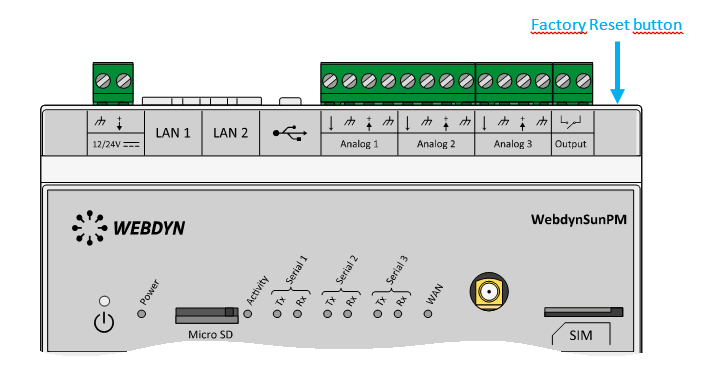 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.


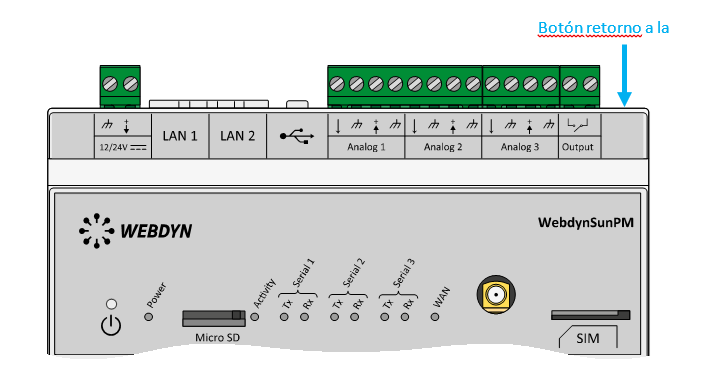 Esperar. El concentrador arrancará con su configuración de fábrica.
Esperar. El concentrador arrancará con su configuración de fábrica.


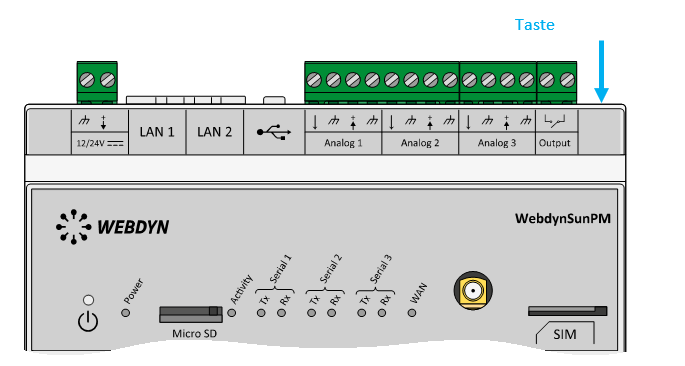 Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.
Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.



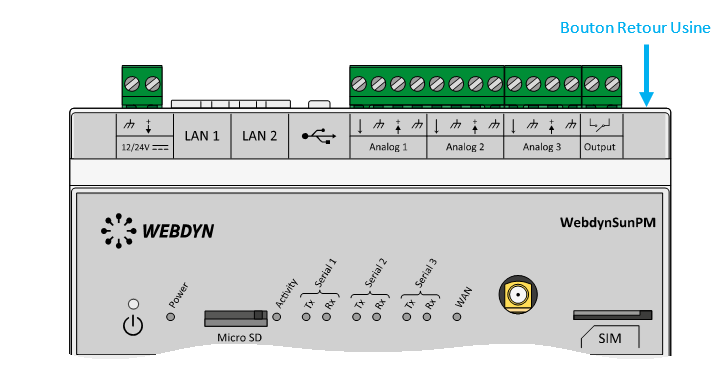 Attendre. Le concentrateur va redémarrer avec sa configuration usine.
Attendre. Le concentrateur va redémarrer avec sa configuration usine.
