Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
Scenario details:
- 8 dry contact sensors need to be monitored. In the status of the entries, they must be sent quickly to an MQTT platform (example Cervello) when a change occurs in one of them. It is also necessary to monitor 2 analog sensors, one of the 0-10V type and the other of the 4-20mA type. Every time the 0-10V sensor varies 100mV or the 4-20mA sensor varies 0.15mA, the value of the sensors should be sent to the MQTT broker
- The status of the modem (coverage, used technology, current IP, etc.) should also be sent periodically, every 60 seconds
- The MQTT broker needs to receive the telemetries in certain topics, as well as the JSON format must have a specific format, so the MTX-Tunnel must be configured appropriately to allow adjusting these requirements
Solution: MTX-Tunnel firmware + MTX-IOT-S [4-N]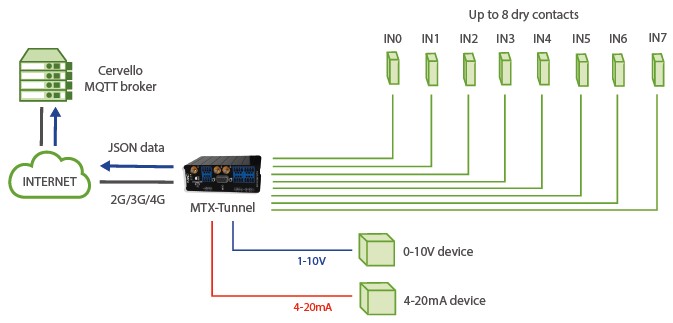
Configuration example (config.txt file) for the indicated scenario:
| Configuration | Observations |
| GPRS_apn: movistar.es GPRS_login: MOVISTAR GPRS_password: MOVISTAR GPRS_timeout: 0 MTX_pin: 0000 MTX_model: 199802407 MTX_mode: none MTX_ping: 30 MTX_pingIP: 8.8.8.8 MTX_numGSMErrors: 180 MTX_TPProtocol: ntp MTX_TPServer: ntp.roa.es MTX_TPServer2: es.pool.ntp.org MTX_TPFormat: unix SMS_allPhones: on SMS_sendIP: on SMS_ATEnabled: on SMS_ATResponse: on MQTT_enabled: on MQTT_server: tcp://broker.mqttdashboard.com:1883 MQTT_id: [IMEI] MQTT_login: MQTT_password: MQTT_attopic1: [IMEI]/AT MQTT_atrtopic: [IMEI]/ATR MQTT_qos: 1 MQTT_keepalive: 60 MQTT_defaultIOQos: 1 MQTT_defaultOTopic: /IOCHANGE DNS_enabled: on DNS_mode: mqtt DNS_exdended: on DNS_period: 60 DNS_mqttTopic: DNS GPIO_mode0: input GPIO_config0: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode1: input GPIO_config1: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode2: input GPIO_config2: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode3: input GPIO_config3: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode4: input GPIO_config4: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode5: input GPIO_config5: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode6: input GPIO_config6: mqtt;2;0 GPIO_mode7: input GPIO_config7: mqtt;2;0 ADC_mode0: voltage ADC_config0: mqtt;100;0 ADC_mode1: current ADC_config1: mqtt;150;0 |
GPRS APN provided by GSM operator GPRS Login GPRS Password Modem is permanently connected to GPRS PIN if it has one Device model Gateways used Every 30 minutes PING check Google IP (f.e.) to ping Reset if no registry on GSM network in 1800 secs. Time synch protocol Time server Time server backup Unix time format IP by SMS authorized IP by SMS authorized AT by SMS allowed SMS AT responses activated MQTT service MQTT broker, format protocol://url:port Device ID in broker Username Password MTX topic to recieve AT commands Topic where MTX sends responses to AT commands QoS established Keepalive MQoS to inform of output changes in real time MQTT topic to inform of output changes in real time DNS to send status Sending mode Also sending GPIOs and ADCs Period of sending, also when data changes Topic to send status data GPIO0 configured as an input GPIO0 MQTT configuration GPIO1 configured as an input GPIO1 MQTT configuration GPIO2 configured as an input GPIO2 MQTT configuration GPIO3 configured as an input GPIO3 MQTT configuration GPIO4 configured as an input GPIO4 MQTT configuration GPIO5 configured as an input GPIO5 MQTT configuration GPIO6 configured as an input GPIO6 MQTT configuration GPIO7 configured as an input GPIO7 MQTT configuration ADC0 as voltage input ADC0 MQTT configuration ADC0 as current input ADC1 MQTT configuration |
Details:
-
The configuration of the inputs as “mqtt; 2; 0” indicates the following. Remember that all parameters are separated by semicolons ;
“mqtt” > The input is configured to send the states of the digital inputs by MQTT
“2” > The 2 indicates that the digital input is configured to send an MQTT message both by activating the input (when it closes, bringing it to ground) and by deactivating the input (when it opens). If you want to send an MQTT message only when closing the entry (bringing it to ground), you should indicate a value of “1”
“0” > Indicates the timeout of the digital input. This means that the change of the digital input will be sent whenever it occurs. If, for example, a value of “10” were configured, as is the case with GPIO4 and GPIO5, even if there are multiple activations in the digital input, more than 1 MQTT message will never be sent in those 10 seconds -
The standard format for sending Digital input messages follows the JSON structure shown in the following example:
{
“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,
“TYPE”:”GPIO”,
“TS”:” 2020-02-08T18:35:15Z”
“ID”:”0”,
“VALUE”:1,
“DIR”:”INPUT”
}Where:
– IMEI: indicates the IMEI of the MTX modem
– TYPE: indicates the type of frame. “GPIO” is for digital I / O frames
– TS: Timestamp (unix format specified in MTX_TPFormat)
– ID: indicates the index of the GPIO (0 = GPIO0, 1 = GPIO1 …, 7 = GPIO7)
– VALUE: indicates the value of the input (0,1)
– DIR: indicates the type of pin (INPUT / OUTPUT) -
The standard sending format of the messages related to analog inputs follow the JSON structure shown in the following example:
{
“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,
“TYPE”:”ADC”,
“TS”:” 2020-02-08T19:15:12Z”
“ID”:0,
“VALUE”:7750
“MODE”:”voltage”
}Where:
– IMEI: indicates the IMEI of the MTX modem
– TYPE: indicates the type of frame. ADC = analog input
– TS: Timestamp (unix format specified in MTX_TPFormat)
– ID: indicates the ADC index (0 = ADC0.1 = ADC1)
– VALUE: indicates the value of the input (in mV or mA)
– MODE: indicates the working mode of the input (“voltage” / “current”) -
The data of the digital inputs / outputs configured as “mqtt” are sent to the topic configured in the parameter “MQTT_defaultIOTopic” and QoS specified in the parameter “MQTT_defaultIOQos”
-
DNS frames, state frames, would have a format like the one shown in the following example:
{“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,”TYPE”:”DNS”,”TS”:”2020-02-09T13:02:24Z”,”P”:””,”IP”:”95.126.2.167”,”CSQ”:9,”TECH”:”4G”,”VER”:”11.00”,”AUX”:””,”MOD”:”MTX-IOT-4G-S”} -
Customizing the JSON and the Topics. Now imagine that you want to send the DNS frames in the json format:
{“data”:
{“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,”TYPE”:”DNS”,”TS”:”2020-02-09T13:04:25Z”,”P”:””,”IP”:”95.126.2.167”,”CSQ”:9,”TECH”:”4G”,”VER”:”11.00”,”AUX”:””,”MOD”:”MTX-IOT-4G-S”,“VCC“:12000}
}
We also want to customize the frames of the digital inputs and the analog inputs in the same way.
{“data”:
{“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,”TYPE”:”ADC”,”TS”:”2020-02-09T13:01:21Z”,”ID”:1,”VALUE”:22774,”MODE”:”current”}
}
And we also want to send DNS frames to the topic “topicDNS”, and each GPIO and ADC to a certain topic, for example “topicGPIO0”, “topicGPIO1”, “topicGPIO2”, …. , “TopicGPIO8”, “topicADC0” and “topic ADC1”
Well, for this, the following configuration structure must be added to the file config.txt:
JSON_config1: {“TYPE”:”DNS”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicDNS”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config2:{“TYPE”:”GPIO0”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO0”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config3: {“TYPE”:”GPIO1”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO1”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config4: {“TYPE”:”GPIO2”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO2”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config5: {“TYPE”:”GPIO3”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO3”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config6: {“TYPE”:”GPIO4”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO4”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config7: {“TYPE”:”GPIO5”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO5”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config8: {“TYPE”:”GPIO6”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO6”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config9: {“TYPE”:”GPIO7”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO7”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}JSON_config10:{“TYPE”:”GPIO8”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO8”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config11: {“TYPE”:”ADC0”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicADC0”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config12: {“TYPE”:”ADC1”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicADC1”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
With the previous configuration we managed to encapsulate the standard JSON sent by the MTX-Tunnel, in another custom JSON. Let’s break down an example:
JSON_config1: {“TYPE”:”DNS”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicDNS”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
This setting indicates:
TYPE: Tipo de trama que se pretende formatear. En este caso la trama “DNS”.
MQTT: Parámetros de MQTT que se utilizarán para dicha trama (en caso de no especificar el JSON
MQTT, se toma como topic el especificado en DNS_mqttTopic y el QoS será “0” para esta trama
FORMAT: Indica el formato que se pretende enviar. MTX-Tunnel utilizará el formato indica, SUBSTITUYENDO el texto indicado en “JSON-MTXTUNNEL” (comillas incluidas) por la trama original DNS que utiliza el MTX-Tunnel.
This setting indicates:
{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
The red highlighted text will be replaced by the standard JSON for DNS frames.
{“data”:
{“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,”TYPE”:”DNS”,”TS”:”2020-02-09T13:04:25Z”,”P”:””,”IP”:”95.126.2.167”,”CSQ”:9,”TECH”:”4G”,”VER”:”11.00”,”AUX”:””,”MOD”:”MTX-IOT-4G-S”,“VCC“:12000}
}
Another example:
JSON_config2:{“TYPE”:”GPIO0”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPIO0”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
This configuration indicates:
TYPE: Type of frame to be formatted. In this case the “GPIO0” frame. (Note that for GPIO and ADC frames, the index of the associated entry must be specified in TYPE, i.e. GPIOx and ADCx)
MQTT: MQTT parameters to be used for this frame (in case you don’t specify the JSON
MQTT, for I / O frames, the one specified in MQTT_defaultIOTopic is taken as topic and the QoS will be the one specified in MQTT_defaultIOQos for this frame.
FORMAT: Indicates the format to be sent. MTX-Tunnel will use the format indicated, SUBSTITUTING the text indicated in “JSON-MTXTUNNEL” (quotes included) by the original DNS frame used by the MTX-Tunnel
That is, for this new plot format:
{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
The red highlighted text will be replaced by the standard JSON for DNS frames.
{“data”:
{
“IMEI”:”354033091487838”,”TYPE”:”GPIO”,”TS”:” 2020-02-08T18:35:15Z”,”ID”:”0”,
“VALUE”:1,”DIR”:”INPUT”
}
}
MTX-Tunnel uses various frame types: DNS, GPIOx, ADCx as seen in the previous paragraphs, but also sends other types of data such as IOS (I / O datalogger), GPS (GPS positioning), MODB (modbus data ), TEMP (temperature probe readings), POWER (external power status) and SERIAL (serial datalogger)
All JSON types can be customized, including TOPIC and QoS (in case of using MQTT), adding in the file config.txt, the following configurations in the JSON_config parameters
JSON_config13: {“TYPE”:”IOS”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicIOS”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config14: {“TYPE”:”GPS”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicGPS”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config15:{“TYPE”:”MODB”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicMODB”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config16: {“TYPE”:”TEMP”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicTEMP”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config17: {“TYPE”:”POWER”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicPOWER”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}
JSON_config18:{“TYPE”:”SERIAL”,”MQTT”:{“TOPIC”:”topicSERIAL”,”QOS”:1},”FORMAT”:{“data”:”JSON-MTXTUNNEL”}}



 Geben Sie den Verbindungsmodus „ethernet“ oder „modem“ ein:
Geben Sie den Verbindungsmodus „ethernet“ oder „modem“ ein:
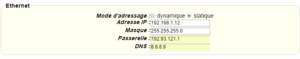
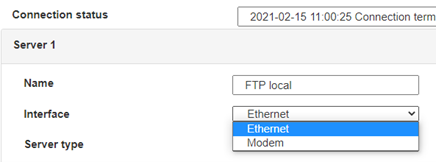 Stellen Sie bei einer Ethernet-Konfiguration sicher, dass die IP-Parameter mit dem Serverzugriff entsprechend der lokalen Netzwerkkonfiguration des Hubs kompatibel sind. Bei einer Ethernet-Verbindung muss die Konfiguration mit der lokalen Netztopologie des Hubs kompatibel sein, damit dieser auf die Server zugreifen kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt über die Konfigurationsseite „Networks“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.3: „Netzwerke (Networks)“).
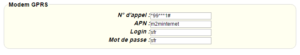
Bei einer Modemverbindung muss das Modem korrekt konfiguriert sein, bevor eine Verbindung hergestellt werden kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt auf der Konfigurationsseite „Modem“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.4: „Modem“).
Die minimal zu konfigurierenden Serverparameter sind folgende:
Stellen Sie bei einer Ethernet-Konfiguration sicher, dass die IP-Parameter mit dem Serverzugriff entsprechend der lokalen Netzwerkkonfiguration des Hubs kompatibel sind. Bei einer Ethernet-Verbindung muss die Konfiguration mit der lokalen Netztopologie des Hubs kompatibel sein, damit dieser auf die Server zugreifen kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt über die Konfigurationsseite „Networks“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.3: „Netzwerke (Networks)“).
Bei einer Modemverbindung muss das Modem korrekt konfiguriert sein, bevor eine Verbindung hergestellt werden kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt auf der Konfigurationsseite „Modem“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.4: „Modem“).
Die minimal zu konfigurierenden Serverparameter sind folgende:
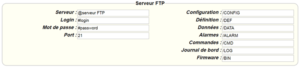
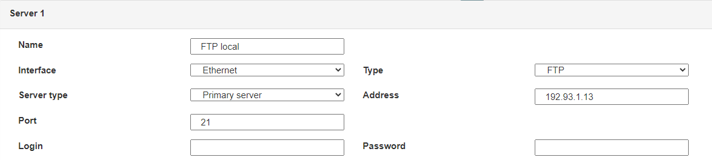 Diese Felder müssen konfiguriert werden: „Interface“, „Type“, „Server type“, „Address“, „Port“, „Login“ und „Password“.
In den übrigen Feldern können die Standardwerte beibehalten werden, solange die Verzeichnisse zuvor korrekt angelegt wurden. Weitere Einzelheiten siehe Kapitel 3.1.2: „Konfigurationsdateien“.
Diese Felder müssen konfiguriert werden: „Interface“, „Type“, „Server type“, „Address“, „Port“, „Login“ und „Password“.
In den übrigen Feldern können die Standardwerte beibehalten werden, solange die Verzeichnisse zuvor korrekt angelegt wurden. Weitere Einzelheiten siehe Kapitel 3.1.2: „Konfigurationsdateien“.
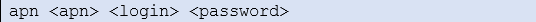



 Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.
Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.