Suchen Sie etwas anderes?
Scenario details:
- We have a PLC Modbus RTU. This PLC has a series of variables/records (for example, a temperature value and 3 meters, etc.) in its internal memory, which must be periodically read and sent to a Web server
- In order to read said records, the MTX-Tunnel must periodically poll the PLC, every 15 minutes, via an RS485serial port. The records to be read are: for temperature, record nº20, and for meters the records in 21, 22 y 23 respectively
- The MTX-Tunnel must send the records value to a web server via HTTP GET using a JSON object after every reading, but must be able, in case of a 2G/3G/4G communications failure, to store up to 1500 records in its flash memory that will be sent once communications are restored
- The PLC has a serial port RS232 that is used to update the firmware. Access to the PLC programming port must be possible at any given time. For this, the RS232 port of the MTX-4GJAVA-IOT-STD-N modem will be used
Solution: MTX-Tunnel firmware + MTX-Java-IoT/MTX-Java-T/MTX-Java-T2
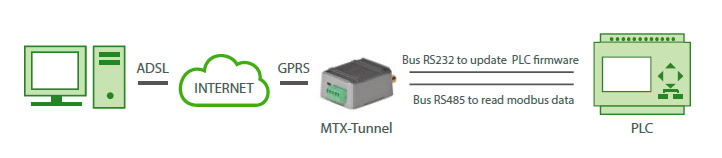
EXAMPLE of settings (file config.txt) for such scenario:
| Configuration | Observations |
| COMM_baudrate: 9600 COMM_bitsperchar: 8 COMM_autorts: on COMM_autocts: on COMM_stopbits: 1 COMM_parity: none COMM2_baudrate: 9600 COMM2_bitsperchar: 8 COMM2_autorts: off COMM2_autocts: off COMM2_stopbits: 1 COMM2_parity: none GPRS_apn: movistar.es GPRS_login: MOVISTAR GPRS_password: MOVISTAR GPRS_timeout: 0 MTX_PIN: 0000 MTX_mode: server MTX_model: MTX-4G-JAVA-IOT-STD-N MTX_portAux: modbusmaster MTX_TPProtocol: ntp MTX_TPServer: ntp.roa.es MTX_TPServer2: es.pool.ntp.org MTX_ping: 35 MTX_pingIP: 8.8.8.8 TCP_port: 20010 SMS_allPhones: on SMS_sendIP: on SMS_ATEnabled: on SMS_ATResponse: on FIREWALL_enabled: off TELNET_enabled: on TELNET_login: user TELNET_password: 1234 TELNET_firewall: off LOGGER_enabled: on LOGGER_password: ID00001 LOGGER_server: www.miservidorWeb.com/json.asp?data= LOGGER_registerSize: 300 LOGGER_numRegistersFlash: 1500 LOGGER_httpMode: getjson MODBUS_address: 1 MODBUS_start: 20 MODBUS_numwords: 4 MODBUS_period: 900 |
Data rate Number of bits There is flow control There is flow control 1 stop bit No parity Serial port baud rate Number of bits No flow control No flow control 1 stop bit No parity APN GPRS from your network operator GPRS Login GPRS Password Modem is always GPRS connected SIM Card PIN Gateway activated for the PLC upgrade MTX modem model AUXILIAR COM port used as master modbus Time synch. protocol Time server Backup time server Ping every 35 minutes without comms IP address to ping TCP port for upgrade firmware gateway All phone numbers are authorized IP sent to phone which called or “on” SM Remote AT commands by SMS enabled Modem response to AT command with SMS Any IP will be able to connect to the modem Telnet is activated Telnet login Telnet password Any IP will be able to connect to the MTX We enable the MTX Logger, to store the records Password field can be used as ID device Server URL, will receive JSON data Register size Maximum number of records in MTX Sending data mode HTTP GET (JSON) Modbus address of device to be read Address of first modbus record to be read Number of records read from each meter Frequency of readings in seconds |
Details:
- The summary of this example is as follows. The modem periodically reads, every 15 minutes, a series of PLC ModBus records and sends them to a web server (to the URL specified in the LOGGER_server parameter) via a JSON object. In cases where a record cannot be sent (because at that moment there is no GPRS coverage or because the server is down) it stores the records in the memory to send them later. Using Telnet it is possible to directly connect to the device and check/change the PLC records in real time (to do so please read the AT^MTXTunnel=getmodbus and AT^MTXTUNNEL=setmodbus commands laid out in this manual)
- The JSON object sent to the URL specified en LOGGER_server is codified as follows:
{“IMEI”:353234028103206,”P”:”ID00001”,”A”:1,”TS”:”20/08/12 08:31:44”,”ST”:20,”V1”:23,”V2”:275,”V3”:274,”V4”:32765}That is, the web server receives a JSON object with the modem’s IMEI (IMEI), a password field (P) that can also be used to identify the device (if you do not want to use the IMEI), the modbus address (A), the time stamp (TS) of when the modbus data has been read, the initial address of the read variables (ST) and V1,V2, … with each of the read variables.
- For the GPRS-Series gateway of the PLC firmware updater we have chosen to work in Server mode (MTX_mode: server) so it is very simple to remotely connect to the MTX-Tunnel via the usual PLC firmware updater, simply stating the IP address and MTX-Tunnel port (if the IP is not fixed, it can be obtained through a missed call, an SMS or even using DynDNS among other options). If your PLC firmware updater does not allow you to enter an IP address, but only a COM port, you can use a virtual COM port such as the one shown in Annex 9
- At the end of the manual you will find how to configure the internal microswitch to activate the RS485 bus of this modem model



 Geben Sie den Verbindungsmodus „ethernet“ oder „modem“ ein:
Geben Sie den Verbindungsmodus „ethernet“ oder „modem“ ein:
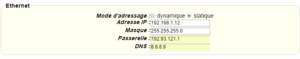
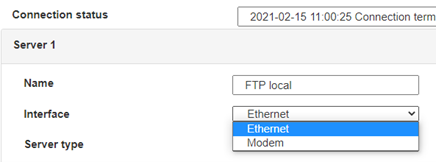 Stellen Sie bei einer Ethernet-Konfiguration sicher, dass die IP-Parameter mit dem Serverzugriff entsprechend der lokalen Netzwerkkonfiguration des Hubs kompatibel sind. Bei einer Ethernet-Verbindung muss die Konfiguration mit der lokalen Netztopologie des Hubs kompatibel sein, damit dieser auf die Server zugreifen kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt über die Konfigurationsseite „Networks“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.3: „Netzwerke (Networks)“).
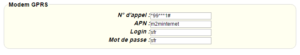
Bei einer Modemverbindung muss das Modem korrekt konfiguriert sein, bevor eine Verbindung hergestellt werden kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt auf der Konfigurationsseite „Modem“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.4: „Modem“).
Die minimal zu konfigurierenden Serverparameter sind folgende:
Stellen Sie bei einer Ethernet-Konfiguration sicher, dass die IP-Parameter mit dem Serverzugriff entsprechend der lokalen Netzwerkkonfiguration des Hubs kompatibel sind. Bei einer Ethernet-Verbindung muss die Konfiguration mit der lokalen Netztopologie des Hubs kompatibel sein, damit dieser auf die Server zugreifen kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt über die Konfigurationsseite „Networks“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.3: „Netzwerke (Networks)“).
Bei einer Modemverbindung muss das Modem korrekt konfiguriert sein, bevor eine Verbindung hergestellt werden kann. Diese Konfiguration erfolgt auf der Konfigurationsseite „Modem“ (siehe Kapitel 3.2.2.4: „Modem“).
Die minimal zu konfigurierenden Serverparameter sind folgende:
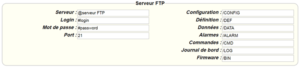
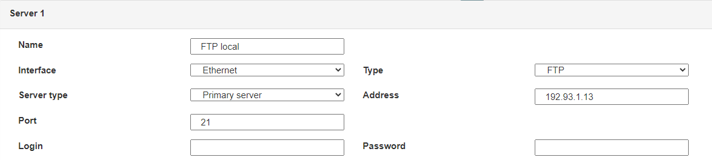 Diese Felder müssen konfiguriert werden: „Interface“, „Type“, „Server type“, „Address“, „Port“, „Login“ und „Password“.
In den übrigen Feldern können die Standardwerte beibehalten werden, solange die Verzeichnisse zuvor korrekt angelegt wurden. Weitere Einzelheiten siehe Kapitel 3.1.2: „Konfigurationsdateien“.
Diese Felder müssen konfiguriert werden: „Interface“, „Type“, „Server type“, „Address“, „Port“, „Login“ und „Password“.
In den übrigen Feldern können die Standardwerte beibehalten werden, solange die Verzeichnisse zuvor korrekt angelegt wurden. Weitere Einzelheiten siehe Kapitel 3.1.2: „Konfigurationsdateien“.



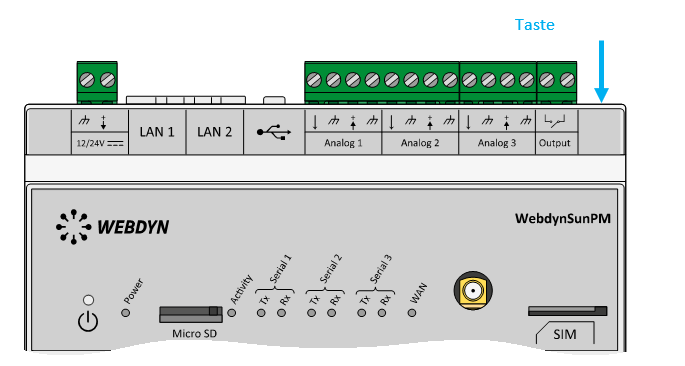 Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.
Warten Sie. Der Hub startet nach ein paar Augenblicken mit der Werkseinstellung neu.